Home / world / France’s Political Upheaval: PM Michel Barnier’s Historic Ouster in No-Confidence Vote
France’s Political Upheaval: PM Michel Barnier’s Historic Ouster in No-Confidence Vote
By: My India Times
3 minutes read 97Updated At: 2024-12-05
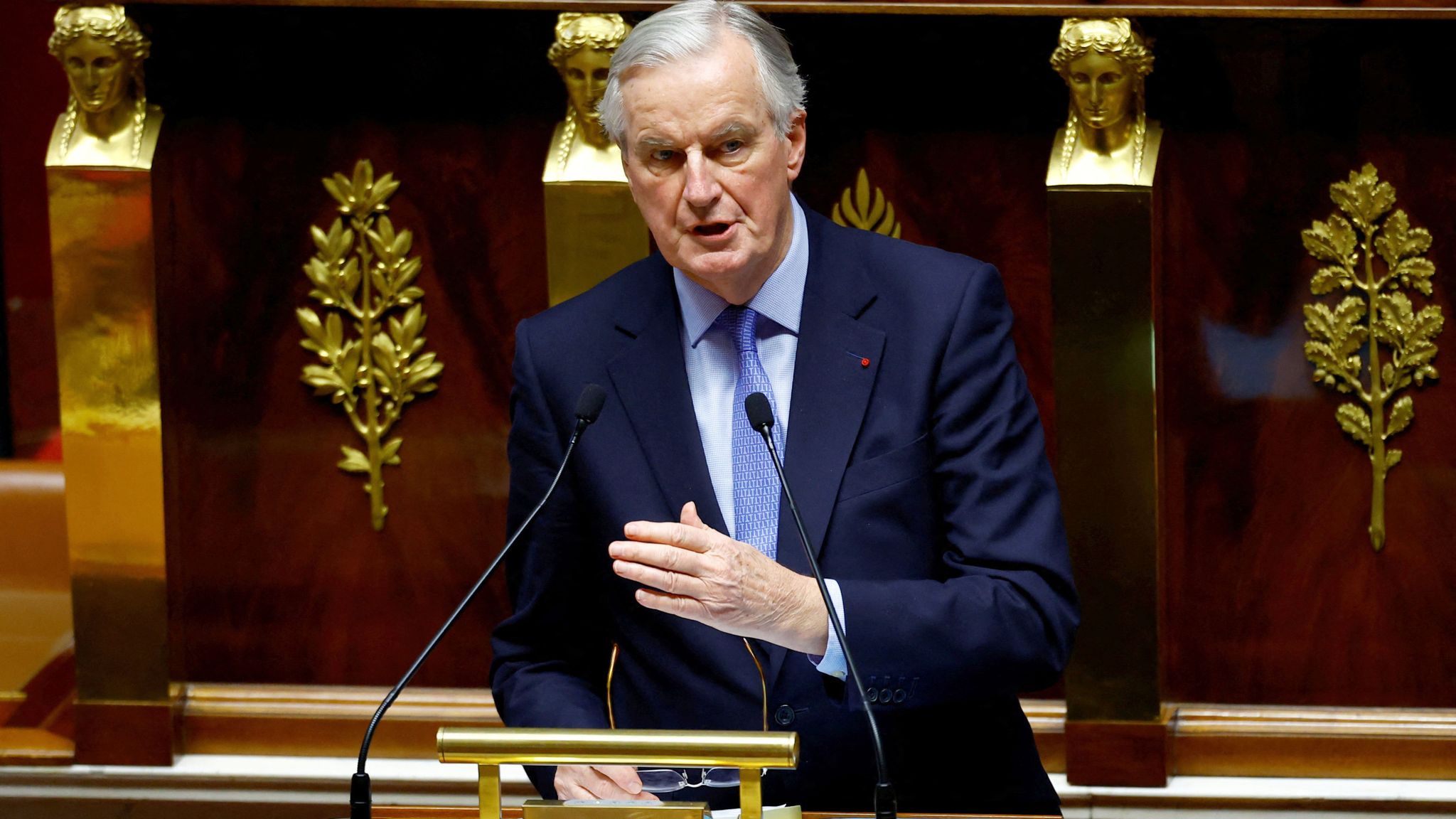

In a seismic shift in French politics, Prime Minister Michel Barnier and his Cabinet have been forced to resign after losing a no-confidence vote—the first such event since 1962. This historic vote not only signifies the conclusion of Barnier’s brief tenure, but also thrusts France into a political crisis that carries substantial repercussions for its domestic stability and its position within the European Union.
A Government Collapses Amid Parliamentary Gridlock
Barnier, appointed in September, became the shortest-serving prime minister in the history of the Fifth Republic. Because no party was able to get a clear majority in the quick legislative elections earlier this year, his administration collapsed. The National Assembly turned into a battleground, with President Macron’s centrist alliance pitted against the far-right National Rally and the left-wing New Popular Front. The no-confidence motion passed with 331 votes, well above the 288 needed, uniting opposition forces in their dissatisfaction with Barnier’s budgetary policies.
The Budget Battle: Key to Barnier’s Downfall
The driving force behind Barnier’s ouster was his controversial attempt to pass a budget that aimed to save €60 billion by bypassing parliamentary approval using Article 49.3 of the French Constitution. This budget, perceived as excessively stringent, sparked significant backlash from both sides of the political spectrum. Left-leaning legislators criticized the reductions to public services, while far-right representatives denounced Barnier’s insufficient emphasis on national interests. This unusual coalition between ideological extremes underscored the pervasive dissatisfaction with Barnier’s governance strategies.
Economic Pressures and France’s Mounting Debt Crisis
France’s ballooning deficit, projected at 6% of GDP this year and potentially rising to 7%, has placed the country under EU scrutiny. Although analysts believe France is not at immediate risk of a Greek-style debt crisis, the rise in borrowing costs has alarmed markets. The fiscal stability of France relies on the implementation of reforms; however, the current political impasse poses a risk to timely action. If this situation remains unresolved, it could lead to higher borrowing costs, complicating debt management and jeopardizing France's standing within the EU.
The Wider Repercussions of Political Unrest
The resignation of Barnier highlights the profound rifts in French politics. With no legal provision for new elections until July 2024, France faces a prolonged period of uncertainty. Investor confidence may waver, and the resulting economic instability could weaken France’s standing within the EU. This crisis also raises serious questions about Macron’s ability to govern effectively, as he faces the daunting task of appointing a new prime minister amid a fractured political landscape.
Macron’s Leadership at a Crossroads
President Macron, determined to complete his term until 2027, must navigate treacherous political waters to appoint a successor who can unify a deeply divided parliament. His challenge lies in finding a prime minister capable of bridging the ideological chasm between opposing factions while ensuring the continuity of his reform agenda. Failure to do so could lead to further legislative deadlock and erode Macron’s political capital.
Potential for a Constitutional Crisis?
The frequent invocation of Article 49.3 to bypass parliamentary votes risks sparking a constitutional crisis. Critics accuse Macron’s government of authoritarian overreach, warning that continued use of this mechanism could undermine public trust in democratic institutions. The growing discontent may also trigger mass protests, adding a layer of social unrest to the already volatile political environment.
Conclusion: A Critical Moment for France and the EU
The fall of Michel Barnier’s government marks a watershed moment in French politics. It tests the resilience of the Fifth Republic and poses serious challenges for France’s economic stability and leadership within the European Union. As Macron seeks to navigate this crisis, the world watches closely, aware that the decisions made in the coming months will shape the future of France and its role on the global stage.
....In a seismic shift in French politics, Prime Minister Michel Barnier and his Cabinet have been forced to resign after losing a no-confidence vote—the first such event since 1962. This historic vote not only signifies the conclusion of Barnier’s brief tenure, but also thrusts France into a political crisis that carries substantial repercussions for its domestic stability and its position within the European Union.
A Government Collapses Amid Parliamentary Gridlock
Barnier, appointed in September, became the shortest-serving prime minister in the history of the Fifth Republic. Because no party was able to get a clear majority in the quick legislative elections earlier this year, his administration collapsed. The National Assembly turned into a battleground, with President Macron’s centrist alliance pitted against the far-right National Rally and the left-wing New Popular Front. The no-confidence motion passed with 331 votes, well above the 288 needed, uniting opposition forces in their dissatisfaction with Barnier’s budgetary policies.
The Budget Battle: Key to Barnier’s Downfall
The driving force behind Barnier’s ouster was his controversial attempt to pass a budget that aimed to save €60 billion by bypassing parliamentary approval using Article 49.3 of the French Constitution. This budget, perceived as excessively stringent, sparked significant backlash from both sides of the political spectrum. Left-leaning legislators criticized the reductions to public services, while far-right representatives denounced Barnier’s insufficient emphasis on national interests. This unusual coalition between ideological extremes underscored the pervasive dissatisfaction with Barnier’s governance strategies.
Economic Pressures and France’s Mounting Debt Crisis
France’s ballooning deficit, projected at 6% of GDP this year and potentially rising to 7%, has placed the country under EU scrutiny. Although analysts believe France is not at immediate risk of a Greek-style debt crisis, the rise in borrowing costs has alarmed markets. The fiscal stability of France relies on the implementation of reforms; however, the current political impasse poses a risk to timely action. If this situation remains unresolved, it could lead to higher borrowing costs, complicating debt management and jeopardizing France's standing within the EU.
The Wider Repercussions of Political Unrest
The resignation of Barnier highlights the profound rifts in French politics. With no legal provision for new elections until July 2024, France faces a prolonged period of uncertainty. Investor confidence may waver, and the resulting economic instability could weaken France’s standing within the EU. This crisis also raises serious questions about Macron’s ability to govern effectively, as he faces the daunting task of appointing a new prime minister amid a fractured political landscape.
Macron’s Leadership at a Crossroads
President Macron, determined to complete his term until 2027, must navigate treacherous political waters to appoint a successor who can unify a deeply divided parliament. His challenge lies in finding a prime minister capable of bridging the ideological chasm between opposing factions while ensuring the continuity of his reform agenda. Failure to do so could lead to further legislative deadlock and erode Macron’s political capital.
Potential for a Constitutional Crisis?
The frequent invocation of Article 49.3 to bypass parliamentary votes risks sparking a constitutional crisis. Critics accuse Macron’s government of authoritarian overreach, warning that continued use of this mechanism could undermine public trust in democratic institutions. The growing discontent may also trigger mass protests, adding a layer of social unrest to the already volatile political environment.
Conclusion: A Critical Moment for France and the EU
The fall of Michel Barnier’s government marks a watershed moment in French politics. It tests the resilience of the Fifth Republic and poses serious challenges for France’s economic stability and leadership within the European Union. As Macron seeks to navigate this crisis, the world watches closely, aware that the decisions made in the coming months will shape the future of France and its role on the global stage.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2024-12-05
Tags: world News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel











































































.png)
















.png)







.jfif)




































































































.png)
 (1).png)