Home / india / Baba Saheb Ambedkar: Human Rights Pioneer and Defender of Justice
Baba Saheb Ambedkar: Human Rights Pioneer and Defender of Justice
By: My India Times
2 minutes read 50Updated At: 2024-12-06
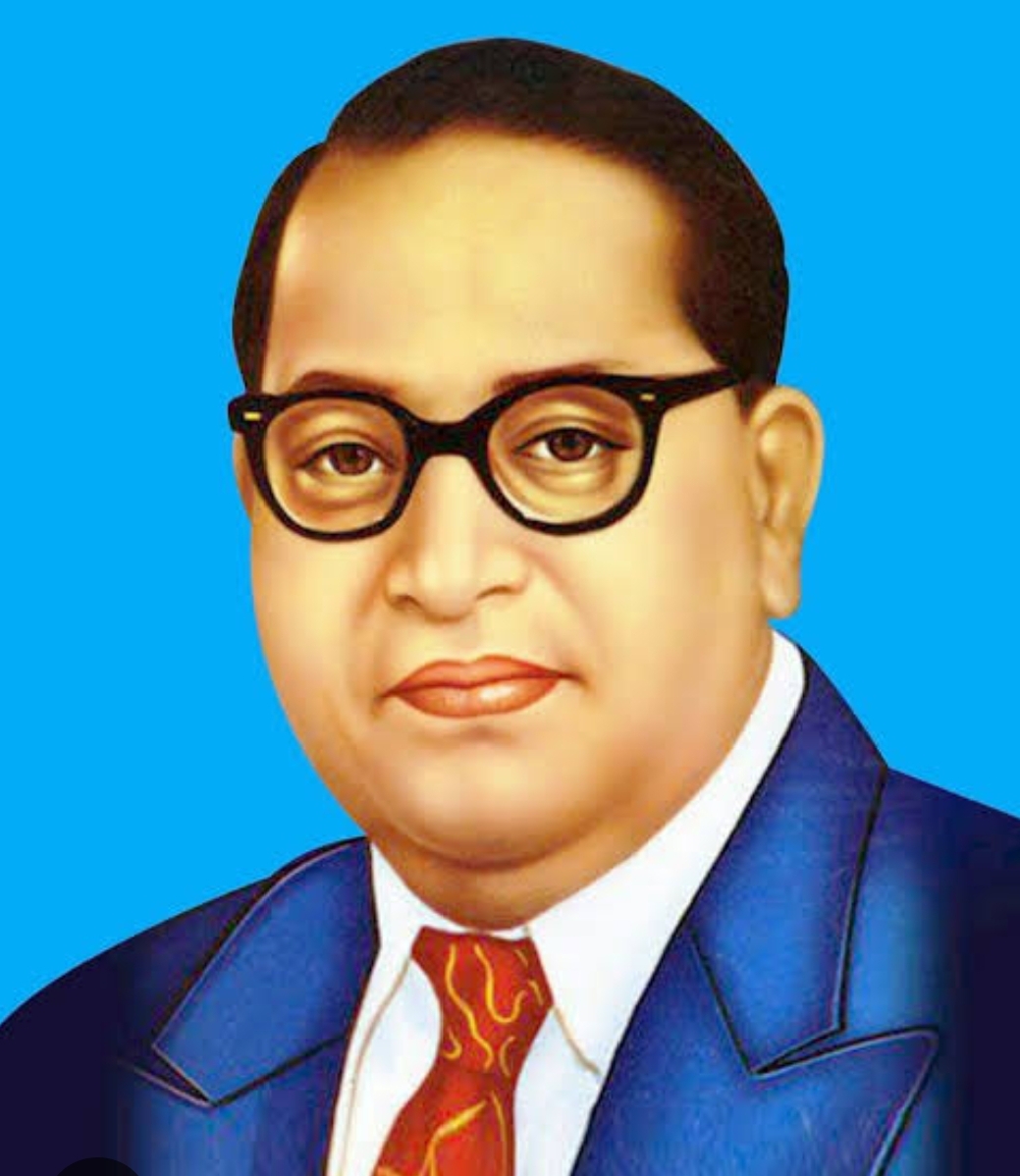

Baba Saheb Ambedkar: Champion of Equality and Human Dignity
Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, widely known as Baba Saheb, stands as a global icon for human rights and justice. Born on 14 April 1891 in a socially marginalized family, Ambedkar emerged as a leader who fought tirelessly for the fundamental rights of the oppressed. His life's work—from battling untouchability to ensuring constitutional rights—continues to inspire movements for justice worldwide. As we observe his death anniversary on 6 December, it is crucial to revisit his revolutionary ideas and their impact on human rights.
Human Rights: A Lifelong Mission
Ambedkar’s fight for human rights began with his own experiences of caste discrimination. Recognizing education as a weapon against inequality, he became one of the most educated leaders of his time. His scholarship and activism laid the foundation for a lifelong mission to eradicate caste-based oppression and promote equality.
Architect of Rights: The Indian Constitution
As the chairman of the Constitution Drafting Committee, Ambedkar was instrumental in embedding human rights into the Indian Constitution. He advocated for the abolition of untouchability (Article 17), equal rights regardless of caste, gender, or religion, and protections for marginalized communities through affirmative action. His work ensured that justice, liberty, and equality became fundamental principles of Indian democracy.
Empowering the Marginalized
Ambedkar’s activism extended beyond legal reforms. He championed women’s rights, recognizing their role in building a just society, and fought for labor rights, securing fair wages and working conditions. His vision of empowerment was deeply rooted in the belief that no society could progress if its weakest members were left behind.
Challenging Oppression through Faith
In a bold move against systemic caste oppression, Ambedkar converted to Buddhism on 14 October 1956. This act was not just personal but a call for social liberation. By embracing Buddhism, he sought a path that upheld human dignity and equality, inspiring millions to follow in his footsteps.
A Legacy That Shapes Human Rights Movements
Ambedkar’s work transcends borders and generations. His fight against caste discrimination resonates with global struggles for racial, gender, and economic justice. His emphasis on education and social reform as tools for empowerment remains a blueprint for human rights advocacy worldwide.
Honoring His Vision Today
As we remember Baba Saheb Ambedkar, we must commit to advancing his mission of equality and justice. His words remind us of our collective responsibility: “Freedom of mind is the real freedom. A person whose mind is not free, though he may not be in chains, is a slave.†Let us honor his legacy by ensuring that human rights are upheld for all, without exception.
Baba Saheb Ambedkar: Champion of Equality and Human Dignity
Dr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, widely known as Baba Saheb, stands as a global icon for human rights and justice. Born on 14 April 1891 in a socially marginalized family, Ambedkar emerged as a leader who fought tirelessly for the fundamental rights of the oppressed. His life's work—from battling untouchability to ensuring constitutional rights—continues to inspire movements for justice worldwide. As we observe his death anniversary on 6 December, it is crucial to revisit his revolutionary ideas and their impact on human rights.
Human Rights: A Lifelong Mission
Ambedkar’s fight for human rights began with his own experiences of caste discrimination. Recognizing education as a weapon against inequality, he became one of the most educated leaders of his time. His scholarship and activism laid the foundation for a lifelong mission to eradicate caste-based oppression and promote equality.
Architect of Rights: The Indian Constitution
As the chairman of the Constitution Drafting Committee, Ambedkar was instrumental in embedding human rights into the Indian Constitution. He advocated for the abolition of untouchability (Article 17), equal rights regardless of caste, gender, or religion, and protections for marginalized communities through affirmative action. His work ensured that justice, liberty, and equality became fundamental principles of Indian democracy.
Empowering the Marginalized
Ambedkar’s activism extended beyond legal reforms. He championed women’s rights, recognizing their role in building a just society, and fought for labor rights, securing fair wages and working conditions. His vision of empowerment was deeply rooted in the belief that no society could progress if its weakest members were left behind.
Challenging Oppression through Faith
In a bold move against systemic caste oppression, Ambedkar converted to Buddhism on 14 October 1956. This act was not just personal but a call for social liberation. By embracing Buddhism, he sought a path that upheld human dignity and equality, inspiring millions to follow in his footsteps.
A Legacy That Shapes Human Rights Movements
Ambedkar’s work transcends borders and generations. His fight against caste discrimination resonates with global struggles for racial, gender, and economic justice. His emphasis on education and social reform as tools for empowerment remains a blueprint for human rights advocacy worldwide.
Honoring His Vision Today
As we remember Baba Saheb Ambedkar, we must commit to advancing his mission of equality and justice. His words remind us of our collective responsibility: “Freedom of mind is the real freedom. A person whose mind is not free, though he may not be in chains, is a slave.†Let us honor his legacy by ensuring that human rights are upheld for all, without exception.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2024-12-06
Tags: india News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel




.webp)


.webp)



































































































.png)
 (1).png)