Home / quick-reads / The Rural-Urban Health Divide: Why Rural Americans Face Shorter Life Expectancies
The Rural-Urban Health Divide: Why Rural Americans Face Shorter Life Expectancies
By: My India Times
4 minutes read 42Updated At: 2025-02-13
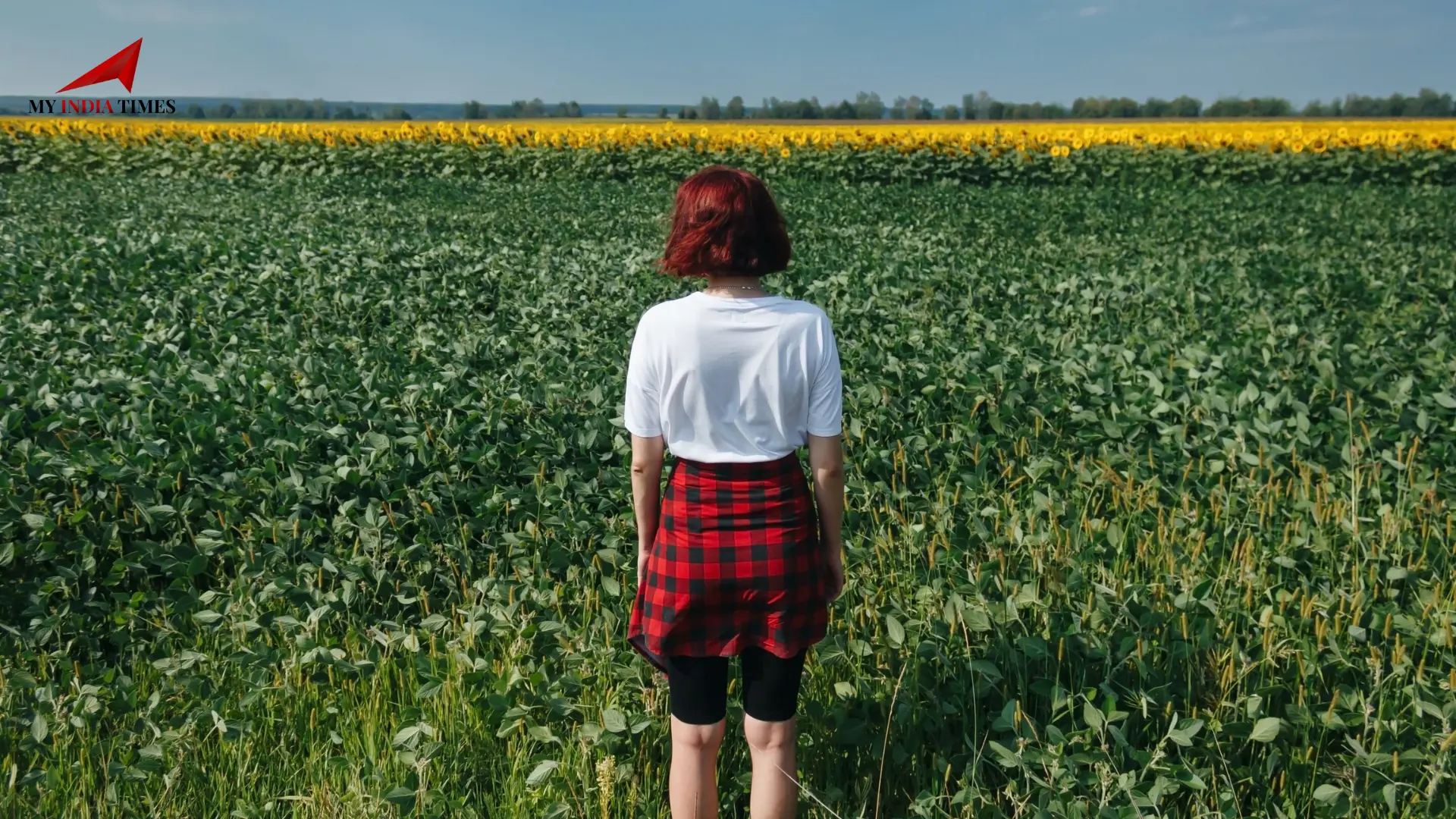

Rural Americans Have a Lower Life Expectancy Than Urban Residents
Recent research has revealed a concerning trend: Rural Americans, particularly men, have significantly shorter life expectancies compared to their urban counterparts. A 60-year-old man living in a rural area is expected to live, on average, two years less than his urban counterpart. Women in rural areas also experience shorter lifespans, though the gap is smaller at six months.
These disparities highlight a growing health crisis in rural America, where factors such as chronic diseases, lifestyle choices, and access to medical care contribute to reduced longevity and overall well-being.
Chronic Diseases and Lifestyle Choices are Key Contributors
One of the primary reasons for the life expectancy gap is the prevalence of chronic health conditions in rural areas. Higher rates of obesity, smoking, heart disease, and high blood pressure significantly impact the health of rural residents. These "silent killers" often go untreated for extended periods due to a lack of awareness, financial constraints, or difficulty accessing healthcare.
Moreover, poor dietary habits and lower levels of physical activity in rural communities exacerbate these health challenges. A lack of fitness facilities, limited access to fresh and nutritious foods, and a culture that often prioritizes hard labor over structured exercise contribute to worsening health outcomes.
The Vanishing Medical Infrastructure in Rural Areas
One of the most pressing issues facing rural Americans is the growing scarcity of medical services. Many rural hospitals and clinics have shut down due to financial difficulties, forcing residents to travel long distances to access healthcare. This creates a major barrier to early detection and treatment of chronic illnesses.
Additionally, there is a critical shortage of healthcare professionals in rural areas. Fewer doctors and specialists mean longer wait times for essential treatments, leading to worsening health conditions over time. The limited presence of mental health services further compounds the problem, increasing the risk of untreated psychological distress, substance abuse, and preventable deaths.
Education Levels Play a Crucial Role in Health Disparities
Education is a significant factor influencing health outcomes, and rural communities lag behind urban areas in this regard. Research shows that only 53% of rural Americans aged 60 and above have education beyond high school, compared to 65% in urban areas.
Higher education levels are often associated with better health literacy, leading to healthier lifestyle choices such as proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adherence to medical advice. Individuals with higher education are also more likely to seek preventive care, reducing the risk of severe health complications later in life.
If rural education levels were on par with urban areas, nearly half of the life expectancy gap could be eliminated. Investing in education, therefore, could be a crucial step in improving health outcomes in rural America.
Economic Struggles and Their Impact on Rural Health
The economic decline in rural areas has played a major role in the deteriorating health of its residents. Job losses due to automation, trade shifts, and the decline of traditional industries have left many rural Americans struggling financially. Economic stress often leads to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Furthermore, financial instability makes healthcare less accessible. Many rural residents are either uninsured or underinsured, leading them to delay medical care until conditions become severe. The high costs of healthcare, combined with the risk of job loss due to chronic illness, create a vicious cycle that further deepens health disparities.
The Connection Between Health and Economic Prosperity
The relationship between health and economic conditions is a two-way street. While economic struggles contribute to poor health, deteriorating health can also worsen economic conditions. Chronic illnesses lead to medical expenses, loss of productivity, and decreased earning potential, further pushing rural families into financial distress.
Additionally, medical emergencies often result in overwhelming debt, forcing many individuals into bankruptcy. A lack of healthcare infrastructure not only affects the well-being of individuals but also weakens the economic stability of entire communities. Addressing rural health disparities is not just a medical issue—it is an economic imperative.
A Call for Comprehensive Health Reforms in Rural America
Addressing the health crisis in rural America requires a multifaceted approach. Expanding access to healthcare facilities, recruiting more medical professionals to rural areas, and investing in public health initiatives are essential steps. Telemedicine can also play a transformative role in bridging the healthcare gap, allowing rural residents to consult with specialists without the burden of travel.
Additionally, improving rural education, promoting healthier lifestyles, and creating economic opportunities can have long-lasting benefits. By tackling the root causes of poor health in rural communities, policymakers can work towards closing the life expectancy gap and ensuring a healthier future for all Americans, regardless of where they live.
The rural-urban health divide is a growing concern, but with strategic efforts, meaningful change is possible. A healthier rural America will lead to a stronger, more resilient nation as a whole.
....
Rural Americans Have a Lower Life Expectancy Than Urban Residents
Recent research has revealed a concerning trend: Rural Americans, particularly men, have significantly shorter life expectancies compared to their urban counterparts. A 60-year-old man living in a rural area is expected to live, on average, two years less than his urban counterpart. Women in rural areas also experience shorter lifespans, though the gap is smaller at six months.
These disparities highlight a growing health crisis in rural America, where factors such as chronic diseases, lifestyle choices, and access to medical care contribute to reduced longevity and overall well-being.
Chronic Diseases and Lifestyle Choices are Key Contributors
One of the primary reasons for the life expectancy gap is the prevalence of chronic health conditions in rural areas. Higher rates of obesity, smoking, heart disease, and high blood pressure significantly impact the health of rural residents. These "silent killers" often go untreated for extended periods due to a lack of awareness, financial constraints, or difficulty accessing healthcare.
Moreover, poor dietary habits and lower levels of physical activity in rural communities exacerbate these health challenges. A lack of fitness facilities, limited access to fresh and nutritious foods, and a culture that often prioritizes hard labor over structured exercise contribute to worsening health outcomes.
The Vanishing Medical Infrastructure in Rural Areas
One of the most pressing issues facing rural Americans is the growing scarcity of medical services. Many rural hospitals and clinics have shut down due to financial difficulties, forcing residents to travel long distances to access healthcare. This creates a major barrier to early detection and treatment of chronic illnesses.
Additionally, there is a critical shortage of healthcare professionals in rural areas. Fewer doctors and specialists mean longer wait times for essential treatments, leading to worsening health conditions over time. The limited presence of mental health services further compounds the problem, increasing the risk of untreated psychological distress, substance abuse, and preventable deaths.
Education Levels Play a Crucial Role in Health Disparities
Education is a significant factor influencing health outcomes, and rural communities lag behind urban areas in this regard. Research shows that only 53% of rural Americans aged 60 and above have education beyond high school, compared to 65% in urban areas.
Higher education levels are often associated with better health literacy, leading to healthier lifestyle choices such as proper nutrition, regular exercise, and adherence to medical advice. Individuals with higher education are also more likely to seek preventive care, reducing the risk of severe health complications later in life.
If rural education levels were on par with urban areas, nearly half of the life expectancy gap could be eliminated. Investing in education, therefore, could be a crucial step in improving health outcomes in rural America.
Economic Struggles and Their Impact on Rural Health
The economic decline in rural areas has played a major role in the deteriorating health of its residents. Job losses due to automation, trade shifts, and the decline of traditional industries have left many rural Americans struggling financially. Economic stress often leads to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Furthermore, financial instability makes healthcare less accessible. Many rural residents are either uninsured or underinsured, leading them to delay medical care until conditions become severe. The high costs of healthcare, combined with the risk of job loss due to chronic illness, create a vicious cycle that further deepens health disparities.
The Connection Between Health and Economic Prosperity
The relationship between health and economic conditions is a two-way street. While economic struggles contribute to poor health, deteriorating health can also worsen economic conditions. Chronic illnesses lead to medical expenses, loss of productivity, and decreased earning potential, further pushing rural families into financial distress.
Additionally, medical emergencies often result in overwhelming debt, forcing many individuals into bankruptcy. A lack of healthcare infrastructure not only affects the well-being of individuals but also weakens the economic stability of entire communities. Addressing rural health disparities is not just a medical issue—it is an economic imperative.
A Call for Comprehensive Health Reforms in Rural America
Addressing the health crisis in rural America requires a multifaceted approach. Expanding access to healthcare facilities, recruiting more medical professionals to rural areas, and investing in public health initiatives are essential steps. Telemedicine can also play a transformative role in bridging the healthcare gap, allowing rural residents to consult with specialists without the burden of travel.
Additionally, improving rural education, promoting healthier lifestyles, and creating economic opportunities can have long-lasting benefits. By tackling the root causes of poor health in rural communities, policymakers can work towards closing the life expectancy gap and ensuring a healthier future for all Americans, regardless of where they live.
The rural-urban health divide is a growing concern, but with strategic efforts, meaningful change is possible. A healthier rural America will lead to a stronger, more resilient nation as a whole.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2025-02-13
Tags: quick-reads News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel

Similiar News

US Supreme Court Rejects 26/11 Accused Tahawwur Rana’s Plea to Block Extradition to India
2025-03-08





























































.jfif)








.jpg)
































































































.png)
 (1).png)