Home / covid / HKU5-CoV-2: New Bat Virus Raises Questions About Human Transmission
HKU5-CoV-2: New Bat Virus Raises Questions About Human Transmission
By: My India Times
3 minutes read 51Updated At: 2025-02-24

What is HKU5-CoV-2? A New Bat Coronavirus with Similarities to COVID-19
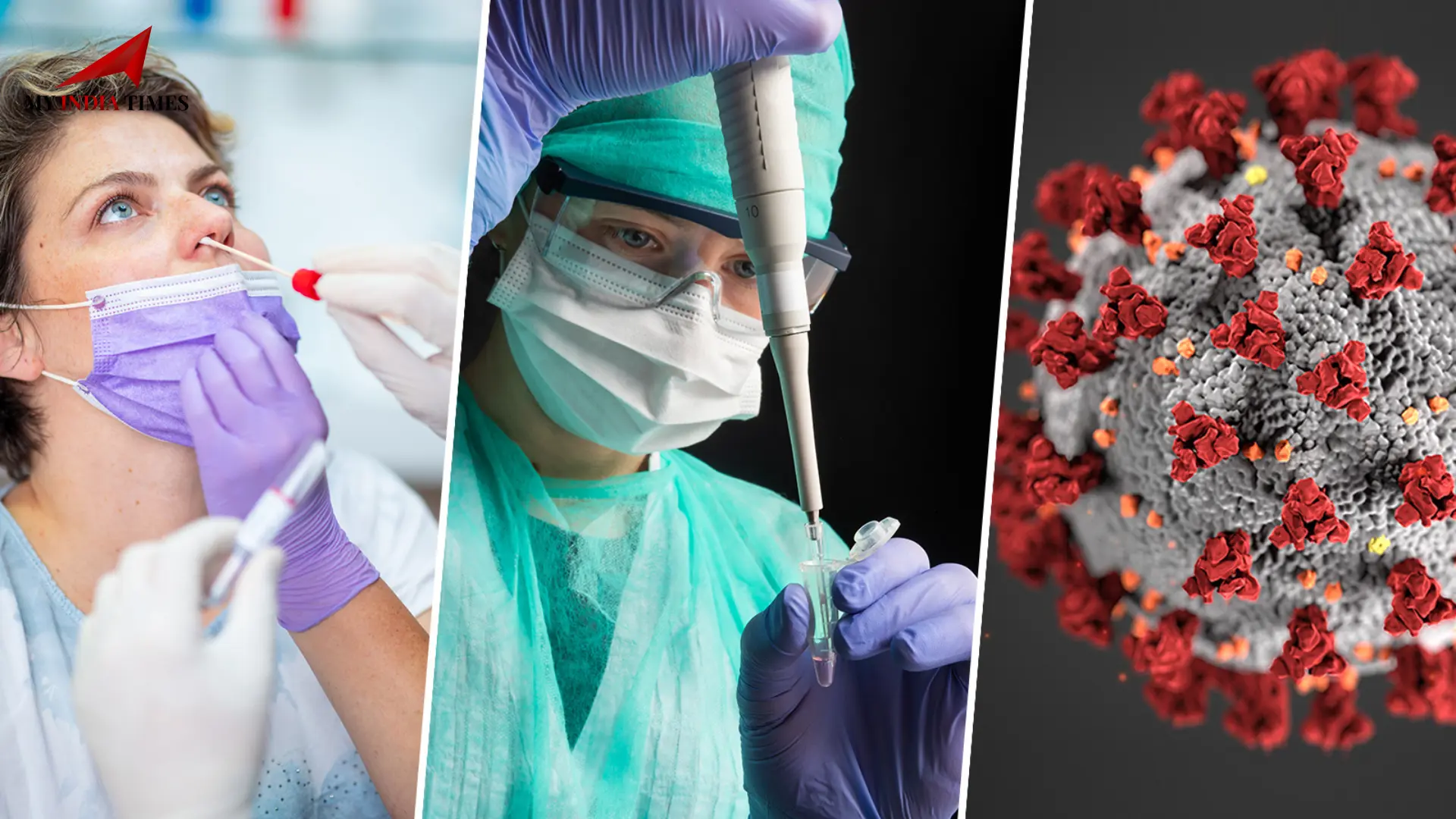
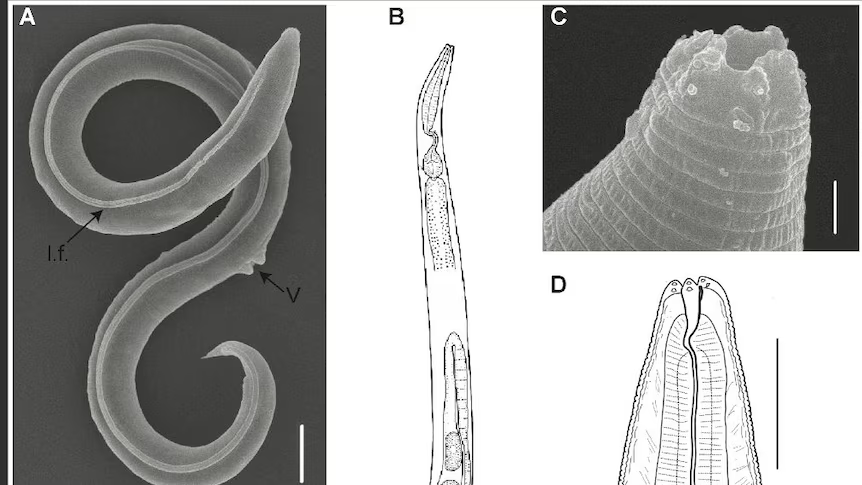
Scientists have recently discovered HKU5-CoV-2, a bat coronavirus that shares key similarities with the virus responsible for COVID-19. Although it can enter human cells using a similar mechanism, experts emphasize that it does not do so as efficiently.
This newly identified virus was studied by researchers at the Wuhan Institute of Virology and detailed in the scientific journal Cell. While the discovery has generated interest, scientists caution that its potential to trigger a new pandemic should not be overstated.
Understanding HKU5-CoV-2: How Does It Infect Human Cells?
HKU5-CoV-2 is a type of coronavirus found in bats, part of a broad family of viruses known to infect mammals and birds. Some coronaviruses, like SARS-CoV-2 (the virus behind COVID-19), have successfully jumped from animals to humans, leading to outbreaks with severe consequences. Others remain limited to animal hosts.
To assess its potential for human transmission, scientists conducted lab experiments using test tubes and models of human intestines and airways. Their findings revealed that HKU5-CoV-2’s spike protein binds to human cell membranes using an enzyme receptor, similar to SARS-CoV-2. This interaction is facilitated by a structural feature known as the furin cleavage site, which enhances the virus’s ability to enter cells.
Is HKU5-CoV-2 a Serious Threat to Humans?
Despite its ability to interact with human cells, HKU5-CoV-2 is significantly less efficient at binding than SARS-CoV-2. The virus exhibits multiple limitations that reduce its ability to infect humans effectively.
As a result, many experts are urging caution in interpreting the findings. The study itself states that “the risk of emergence in human populations should not be exaggerated.” Dr. Michael Osterholm, an infectious disease expert at the University of Minnesota, echoed this sentiment, calling concerns about the virus’s potential for causing a new pandemic “overblown.” He also noted that the human population now has greater immunity to SARS-like viruses, which may offer some protection.
However, despite these reassurances, the discovery had an immediate impact on the financial markets. Reports from Bloomberg indicated that shares of major COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers, including Pfizer, Moderna, and Novavax, rose following the news.
How Might HKU5-CoV-2 Be Treated If It Infects Humans?
While HKU5-CoV-2 does not currently pose a major threat, scientists have explored potential treatment options should it ever evolve to become more infectious in humans.
Monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs have been identified as possible treatments. Antiviral medications work by preventing viral replication, potentially reducing symptoms and illness duration. These drugs are already in use for conditions such as the flu and COVID-19.
Monoclonal antibodies, on the other hand, are lab-engineered proteins designed to target specific viruses. Some monoclonal antibody treatments for COVID-19 were developed to block the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from binding to human cells. While highly effective, their success varies depending on viral mutations, requiring continuous research and development.
The Importance of Vigilance and Research
The discovery of HKU5-CoV-2 highlights the ongoing importance of studying zoonotic viruses—pathogens that have the potential to jump from animals to humans. While this particular virus does not currently pose an immediate risk, continued surveillance and research are crucial to preventing future outbreaks.
By understanding how such viruses evolve and interact with human biology, scientists can stay ahead of potential threats, develop effective treatments, and ensure global preparedness for future pandemics. As new viruses continue to emerge, proactive scientific efforts remain our best defense.
....What is HKU5-CoV-2? A New Bat Coronavirus with Similarities to COVID-19
Scientists have recently discovered HKU5-CoV-2, a bat coronavirus that shares key similarities with the virus responsible for COVID-19. Although it can enter human cells using a similar mechanism, experts emphasize that it does not do so as efficiently.
This newly identified virus was studied by researchers at the Wuhan Institute of Virology and detailed in the scientific journal Cell. While the discovery has generated interest, scientists caution that its potential to trigger a new pandemic should not be overstated.
Understanding HKU5-CoV-2: How Does It Infect Human Cells?
HKU5-CoV-2 is a type of coronavirus found in bats, part of a broad family of viruses known to infect mammals and birds. Some coronaviruses, like SARS-CoV-2 (the virus behind COVID-19), have successfully jumped from animals to humans, leading to outbreaks with severe consequences. Others remain limited to animal hosts.
To assess its potential for human transmission, scientists conducted lab experiments using test tubes and models of human intestines and airways. Their findings revealed that HKU5-CoV-2’s spike protein binds to human cell membranes using an enzyme receptor, similar to SARS-CoV-2. This interaction is facilitated by a structural feature known as the furin cleavage site, which enhances the virus’s ability to enter cells.
Is HKU5-CoV-2 a Serious Threat to Humans?
Despite its ability to interact with human cells, HKU5-CoV-2 is significantly less efficient at binding than SARS-CoV-2. The virus exhibits multiple limitations that reduce its ability to infect humans effectively.
As a result, many experts are urging caution in interpreting the findings. The study itself states that “the risk of emergence in human populations should not be exaggerated.” Dr. Michael Osterholm, an infectious disease expert at the University of Minnesota, echoed this sentiment, calling concerns about the virus’s potential for causing a new pandemic “overblown.” He also noted that the human population now has greater immunity to SARS-like viruses, which may offer some protection.
However, despite these reassurances, the discovery had an immediate impact on the financial markets. Reports from Bloomberg indicated that shares of major COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers, including Pfizer, Moderna, and Novavax, rose following the news.
How Might HKU5-CoV-2 Be Treated If It Infects Humans?
While HKU5-CoV-2 does not currently pose a major threat, scientists have explored potential treatment options should it ever evolve to become more infectious in humans.
Monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs have been identified as possible treatments. Antiviral medications work by preventing viral replication, potentially reducing symptoms and illness duration. These drugs are already in use for conditions such as the flu and COVID-19.
Monoclonal antibodies, on the other hand, are lab-engineered proteins designed to target specific viruses. Some monoclonal antibody treatments for COVID-19 were developed to block the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from binding to human cells. While highly effective, their success varies depending on viral mutations, requiring continuous research and development.
The Importance of Vigilance and Research
The discovery of HKU5-CoV-2 highlights the ongoing importance of studying zoonotic viruses—pathogens that have the potential to jump from animals to humans. While this particular virus does not currently pose an immediate risk, continued surveillance and research are crucial to preventing future outbreaks.
By understanding how such viruses evolve and interact with human biology, scientists can stay ahead of potential threats, develop effective treatments, and ensure global preparedness for future pandemics. As new viruses continue to emerge, proactive scientific efforts remain our best defense.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2025-02-24
Tags: covid News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel














-outbreak in-china.jpg)
























































































.png)
 (1).png)