Home / covid / China Warns of Potential New Coronavirus Threat: HKU5-CoV-2 Identified
China Warns of Potential New Coronavirus Threat: HKU5-CoV-2 Identified
By: My India Times
2 minutes read 47Updated At: 2025-02-24

New Coronavirus Emerges: China Sounds Alarm Over Potential Outbreak
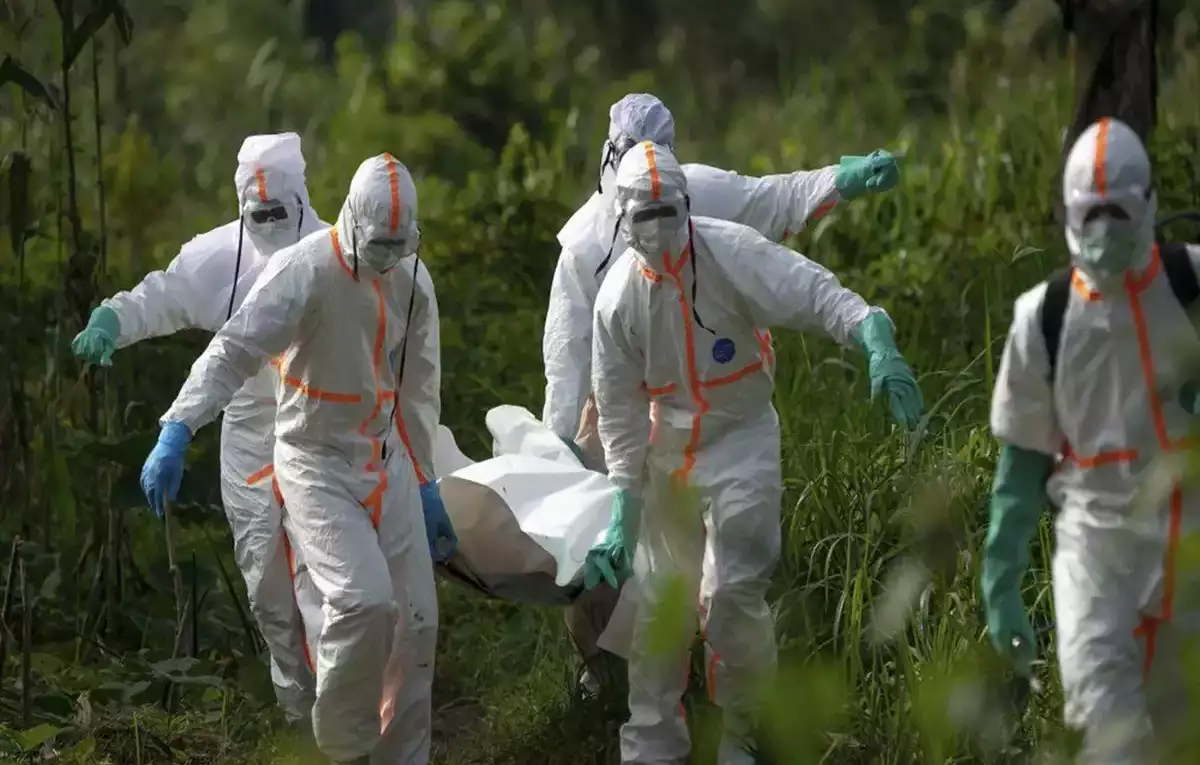
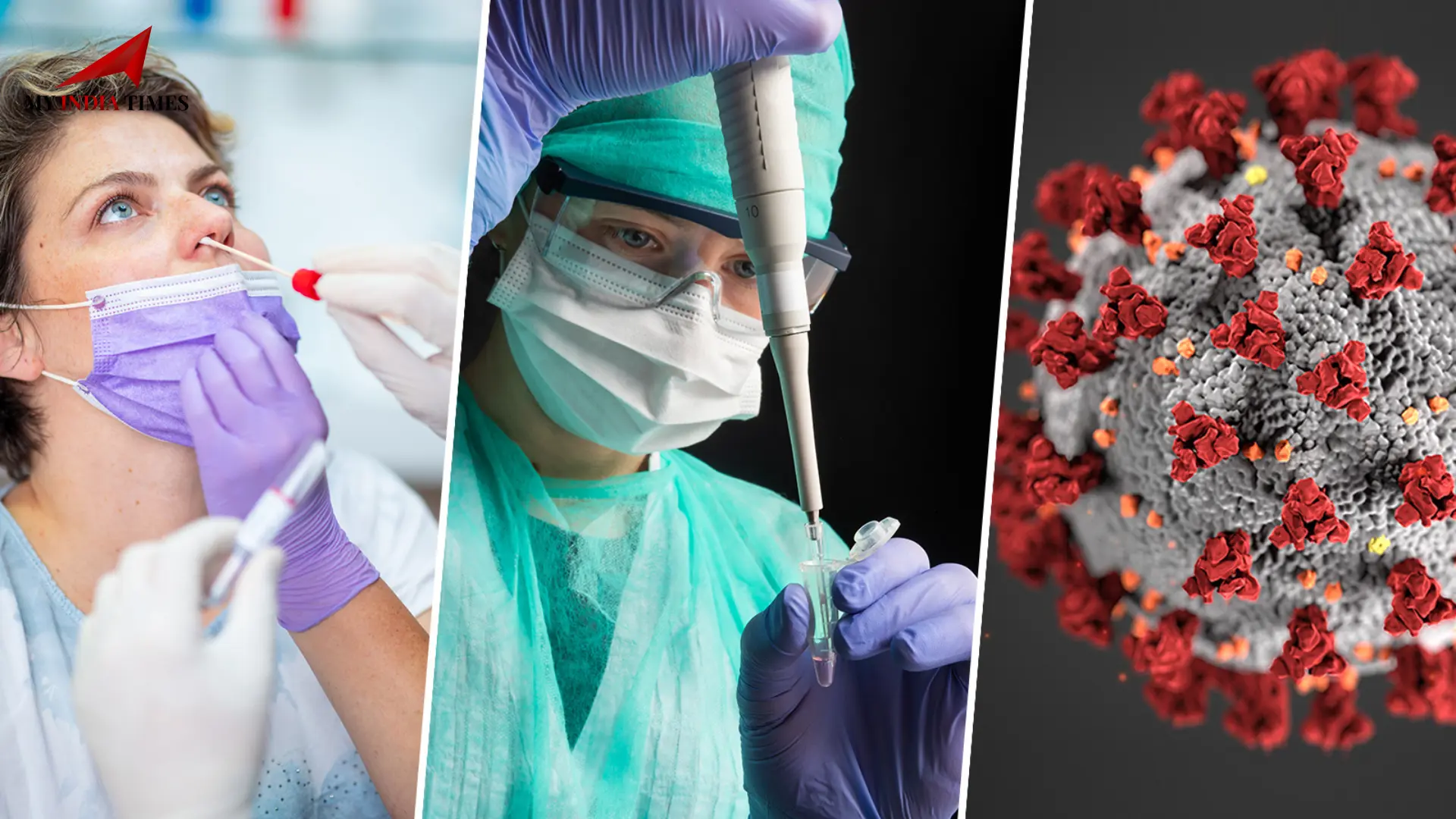
China has recently issued a warning about the discovery of a new coronavirus strain that could pose a potential risk to humans. According to scientific reports, this virus, named HKU5-CoV-2, is believed to have originated in bats and exhibits characteristics similar to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the Covid-19 pandemic.
This discovery has raised alarms among health professionals and international authorities, as the virus exhibits the capability to attach to the human ACE2 receptor, the same pathway utilized by the coronavirus responsible for the global pandemic. Although there have been no reported instances of human transmission to date, scientists emphasize the necessity of ongoing surveillance to avert another possible outbreak.
Discovery of HKU5-CoV-2: A New Generation of Coronaviruses
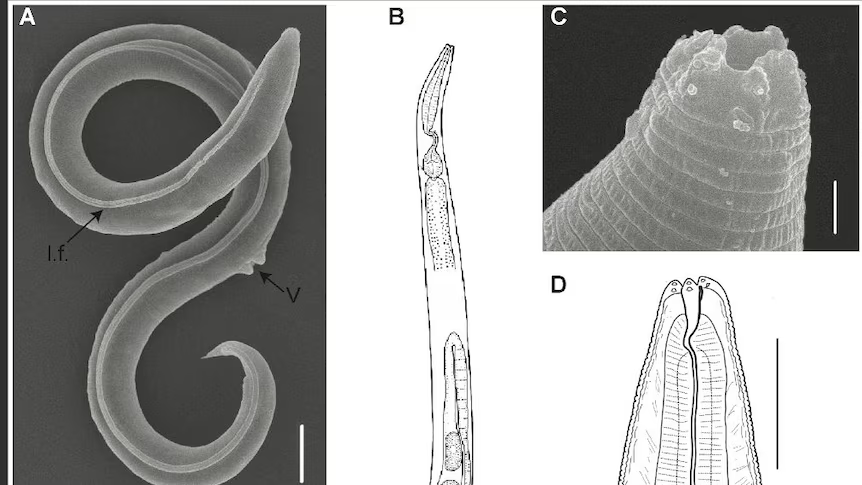
HKU5-CoV-2 is classified as a new generation of the HKU-5 coronavirus and was first identified in Japanese pipistrelle bats in Hong Kong. It belongs to the Merbecovirus subgenus and has been under study for its potential to infect humans.
Researchers from multiple leading institutions, including the Guangzhou Academy of Sciences, Wuhan University, and the Wuhan Institute of Virology, have contributed to this discovery. The findings, led by renowned virologist Shi Zhengli—popularly known as 'Batwoman' for her extensive research on bat-borne viruses—were recently published in the esteemed scientific journal Cell.
Potential Risks of HKU5-CoV-2: How Dangerous Is It for Humans?
While there is still ongoing research regarding the origins and risks of this virus, preliminary findings indicate that HKU5-CoV-2 has the capability to bind to both bat ACE2 and human ACE2 receptors. This adaptation raises concerns about its potential to infect human cells.
Laboratory studies have shown that when isolated from bat samples, HKU5-CoV-2 was able to infect human cells as well as artificially grown cellular structures resembling human respiratory and intestinal tissues. This suggests that the virus has the potential for cross-species transmission, which could pose a health risk if left unmonitored.
How Likely Is an Outbreak? Scientists Assess the Threat Level
Despite concerns about the virus's ability to infect human cells, researchers emphasize that the risk of an immediate outbreak should not be overstated. According to Shi Zhengli’s research team, HKU5-CoV-2 has shown better adaptation to human ACE2 compared to previous coronaviruses but does not yet exhibit the same potency as Covid-19.
The study underscores the need for increased vigilance and continued surveillance to assess potential risks. While the likelihood of a widespread outbreak remains low at present, scientists stress that proactive measures, such as global monitoring and early intervention strategies, are essential to prevent future pandemics.
Preparing for Future Pandemic Threats
The discovery of HKU5-CoV-2 serves as a stark reminder that the threat of emerging infectious diseases remains ever-present. As human activities continue to encroach on wildlife habitats, the risk of zoonotic spillovers increases, necessitating stronger global health policies and research efforts.
By investing in disease surveillance, improving rapid response capabilities, and fostering international scientific collaboration, the world can be better prepared to tackle potential pandemic threats before they escalate into global crises. Continued vigilance, combined with cutting-edge virological research, will play a crucial role in safeguarding global health.
....
New Coronavirus Emerges: China Sounds Alarm Over Potential Outbreak
China has recently issued a warning about the discovery of a new coronavirus strain that could pose a potential risk to humans. According to scientific reports, this virus, named HKU5-CoV-2, is believed to have originated in bats and exhibits characteristics similar to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the Covid-19 pandemic.
This discovery has raised alarms among health professionals and international authorities, as the virus exhibits the capability to attach to the human ACE2 receptor, the same pathway utilized by the coronavirus responsible for the global pandemic. Although there have been no reported instances of human transmission to date, scientists emphasize the necessity of ongoing surveillance to avert another possible outbreak.
Discovery of HKU5-CoV-2: A New Generation of Coronaviruses
HKU5-CoV-2 is classified as a new generation of the HKU-5 coronavirus and was first identified in Japanese pipistrelle bats in Hong Kong. It belongs to the Merbecovirus subgenus and has been under study for its potential to infect humans.
Researchers from multiple leading institutions, including the Guangzhou Academy of Sciences, Wuhan University, and the Wuhan Institute of Virology, have contributed to this discovery. The findings, led by renowned virologist Shi Zhengli—popularly known as 'Batwoman' for her extensive research on bat-borne viruses—were recently published in the esteemed scientific journal Cell.
Potential Risks of HKU5-CoV-2: How Dangerous Is It for Humans?
While there is still ongoing research regarding the origins and risks of this virus, preliminary findings indicate that HKU5-CoV-2 has the capability to bind to both bat ACE2 and human ACE2 receptors. This adaptation raises concerns about its potential to infect human cells.
Laboratory studies have shown that when isolated from bat samples, HKU5-CoV-2 was able to infect human cells as well as artificially grown cellular structures resembling human respiratory and intestinal tissues. This suggests that the virus has the potential for cross-species transmission, which could pose a health risk if left unmonitored.
How Likely Is an Outbreak? Scientists Assess the Threat Level
Despite concerns about the virus's ability to infect human cells, researchers emphasize that the risk of an immediate outbreak should not be overstated. According to Shi Zhengli’s research team, HKU5-CoV-2 has shown better adaptation to human ACE2 compared to previous coronaviruses but does not yet exhibit the same potency as Covid-19.
The study underscores the need for increased vigilance and continued surveillance to assess potential risks. While the likelihood of a widespread outbreak remains low at present, scientists stress that proactive measures, such as global monitoring and early intervention strategies, are essential to prevent future pandemics.
Preparing for Future Pandemic Threats
The discovery of HKU5-CoV-2 serves as a stark reminder that the threat of emerging infectious diseases remains ever-present. As human activities continue to encroach on wildlife habitats, the risk of zoonotic spillovers increases, necessitating stronger global health policies and research efforts.
By investing in disease surveillance, improving rapid response capabilities, and fostering international scientific collaboration, the world can be better prepared to tackle potential pandemic threats before they escalate into global crises. Continued vigilance, combined with cutting-edge virological research, will play a crucial role in safeguarding global health.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2025-02-24
Tags: covid News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel














-outbreak in-china.jpg)
























































































.png)
 (1).png)