Home / art-and-culture / "Roots of Heritage: Madhya Pradesh's Art and Culture as Pillars of Human Rights"
"Roots of Heritage: Madhya Pradesh's Art and Culture as Pillars of Human Rights"
By: My India Times
1 minutes read 25Updated At: 2024-12-20

Madhya Pradesh’s Art and Culture: A Reflection of Human Rights
Madhya Pradesh, the heart of India, is renowned for its rich and diverse art and cultural heritage. Beyond its historical and social importance, this diversity offers a profound perspective on human rights, highlighting the right to identity, expression, and dignity.
1. Gond Art: The Voice of a Community
Gond art is more than a creative expression; it is a celebration of tribal life and their inherent rights. The vibrant patterns and depictions of nature symbolize harmony between humans and the environment, emphasizing the right to coexist.
2. Traditional Crafts: A Path to Economic Freedom
The intricate bamboo and cane work, terracotta pottery, and Dhokra metal casting by tribal artisans exemplify the right to livelihood. These crafts preserve their economic independence and reinforce their dignity in society.
3. Dance and Music: Channels of Cultural Freedom
Folk dances like Bhagoria, Tertahli, and Matki, along with musical instruments like flutes and drums, are vital mediums of cultural expression. They embody the human right to freedom of expression and cultural participation.
4. Festivals and Fairs: A Message of Inclusivity
Events like the Khajuraho Dance Festival and Bhagoria Mela unite people across caste, creed, and religion. These celebrations advocate for social equality and the right to cultural inclusion.
5. Architectural Heritage: Protecting the Past
The magnificent temples of Khajuraho, the Sanchi Stupa, and the Bhimbetka caves stand as symbols of cultural preservation. They emphasize the human right to access and protect our collective heritage.
6. Traditional Attire and Cuisine: Honoring Local Identity
Chanderi and Maheshwari sarees, crafted by local weavers, and delicacies like Dal Bafla and Poha-Jalebi signify the right to celebrate regional identity. These elements promote respect for diversity and community traditions.
A Cultural Tapestry of Rights
Madhya Pradesh’s art and culture are not merely aesthetic assets; they are powerful advocates for human rights. From empowering communities to promoting equality, the state’s traditions serve as a testament to the enduring connection between culture and humanity’s fundamental rights.
....Madhya Pradesh’s Art and Culture: A Reflection of Human Rights
Madhya Pradesh, the heart of India, is renowned for its rich and diverse art and cultural heritage. Beyond its historical and social importance, this diversity offers a profound perspective on human rights, highlighting the right to identity, expression, and dignity.
1. Gond Art: The Voice of a Community
Gond art is more than a creative expression; it is a celebration of tribal life and their inherent rights. The vibrant patterns and depictions of nature symbolize harmony between humans and the environment, emphasizing the right to coexist.
2. Traditional Crafts: A Path to Economic Freedom
The intricate bamboo and cane work, terracotta pottery, and Dhokra metal casting by tribal artisans exemplify the right to livelihood. These crafts preserve their economic independence and reinforce their dignity in society.
3. Dance and Music: Channels of Cultural Freedom
Folk dances like Bhagoria, Tertahli, and Matki, along with musical instruments like flutes and drums, are vital mediums of cultural expression. They embody the human right to freedom of expression and cultural participation.
4. Festivals and Fairs: A Message of Inclusivity
Events like the Khajuraho Dance Festival and Bhagoria Mela unite people across caste, creed, and religion. These celebrations advocate for social equality and the right to cultural inclusion.
5. Architectural Heritage: Protecting the Past
The magnificent temples of Khajuraho, the Sanchi Stupa, and the Bhimbetka caves stand as symbols of cultural preservation. They emphasize the human right to access and protect our collective heritage.
6. Traditional Attire and Cuisine: Honoring Local Identity
Chanderi and Maheshwari sarees, crafted by local weavers, and delicacies like Dal Bafla and Poha-Jalebi signify the right to celebrate regional identity. These elements promote respect for diversity and community traditions.
A Cultural Tapestry of Rights
Madhya Pradesh’s art and culture are not merely aesthetic assets; they are powerful advocates for human rights. From empowering communities to promoting equality, the state’s traditions serve as a testament to the enduring connection between culture and humanity’s fundamental rights.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2024-12-20
Tags: art-and-culture News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel

Similiar News
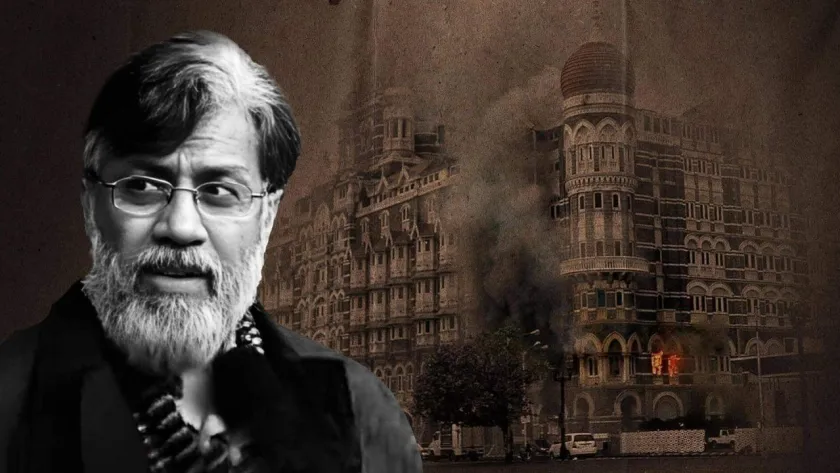

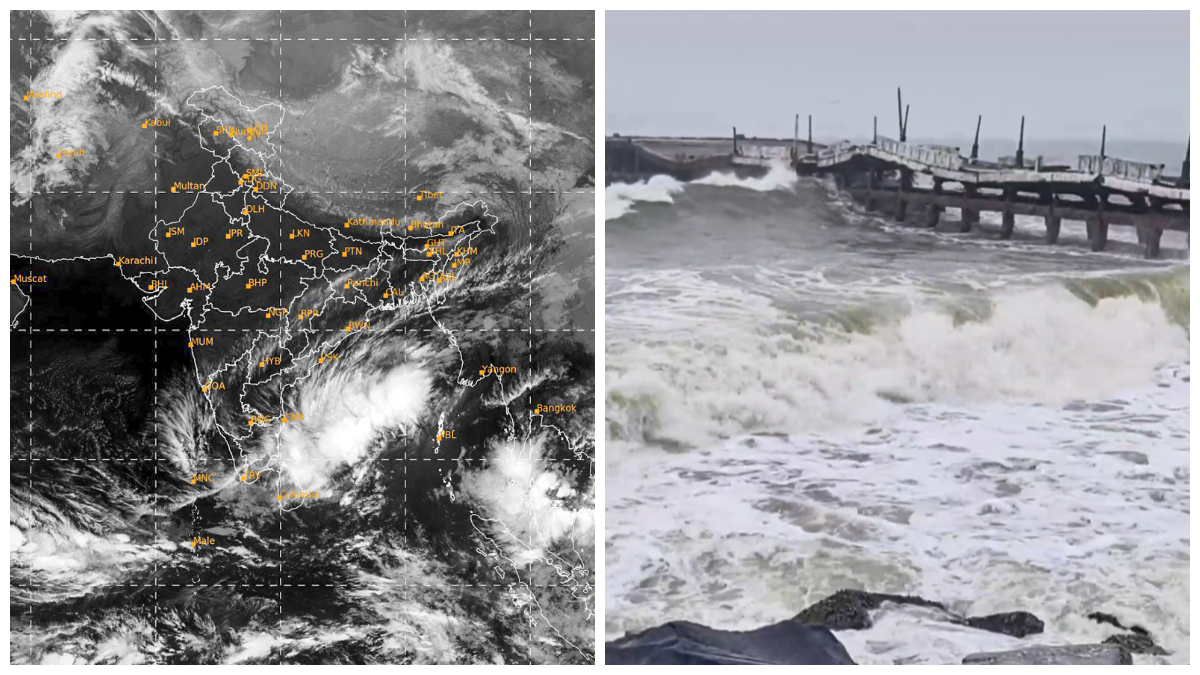
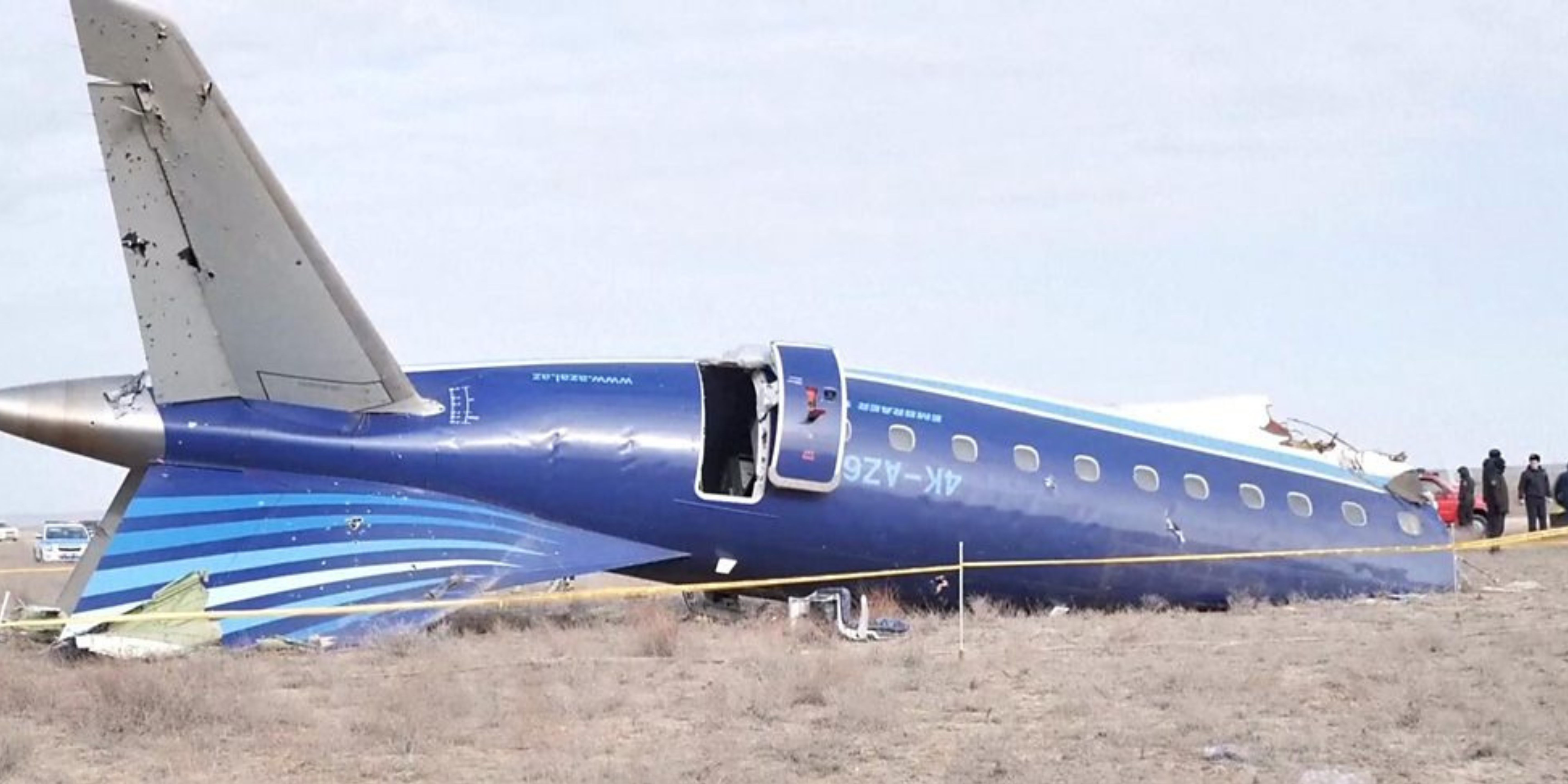
US Supreme Court Rejects 26/11 Accused Tahawwur Rana’s Plea to Block Extradition to India
2025-03-08





























































.jfif)








.jpg)



























































































.png)
 (1).png)