Home / madhya-pradesh / Vulture Census Begins Today in the Tiger State: Why These Birds Are Essential for Humans
Vulture Census Begins Today in the Tiger State: Why These Birds Are Essential for Humans
By: My India Times
5 minutes read 27Updated At: 2025-02-17

India is home to a significant portion of the world’s tiger population, and conservation efforts over the past few decades have yielded some positive results. The population of tigers in India has increased due to various conservation programs like Project Tiger, but this success is not without its challenges. Despite the significant progress made in recent years, tigers continue to face numerous threats, including habitat degradation, illegal poaching, and conflicts with human populations. These challenges could jeopardize the extensive efforts dedicated to the conservation of these magnificent creatures.
Habitat Preservation and Fragmentation
A vital component of tiger conservation is the safeguarding of their natural habitats. India has been proactively engaged in the establishment of tiger reserves; however, these initiatives encounter significant challenges due to deforestation and land encroachment for agricultural purposes. As forests are cleared to accommodate human populations, the subsequent fragmentation of habitats markedly impacts tiger populations. Tigers require large territories to roam freely, hunt, and establish their territory. If these territories are disrupted or too fragmented, their survival becomes uncertain. Experts emphasize the need for connecting isolated forests through wildlife corridors to allow tigers to safely move between habitats.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Poaching remains one of the largest threats to tiger populations in India. The illicit trade in tiger body parts, encompassing skins, bones, and organs, perpetuates illegal poaching, irrespective of the strict regulations enacted to safeguard these majestic animals. The worldwide demand for tiger components, particularly within traditional medicine practices, renders them extremely attractive to poachers. In response, enhanced law enforcement initiatives, including the deployment of advanced technologies like camera traps and drones, have been introduced in tiger reserves. Furthermore, community involvement and educational programs are essential in fostering a protective atmosphere for tigers.
Human-Wildlife Conflict and Coexistence
The increase in human-wildlife conflict presents a significant challenge for tiger conservation. As human populations expand, tigers are increasingly drawn into agricultural regions, resulting in heightened conflict. Instances of tigers attacking livestock often provoke retaliatory actions from local farmers. This conflict not only threatens the tiger population but also creates a tense relationship between wildlife conservationists and the local community. The solution lies in creating buffer zones, where humans and wildlife can coexist safely. Measures like livestock enclosures, compensation for lost animals, and awareness campaigns are crucial in alleviating human-wildlife conflict.
Tiger Monitoring and Population Data
Monitoring tiger populations through national surveys is essential in understanding the dynamics of their numbers and overall health. The annual tiger census provides valuable data on the distribution, population, and behavior of tigers. This data helps conservationists gauge the effectiveness of current strategies and adjust them accordingly. It also helps identify areas of high tiger activity, which can be further protected or restored. Additionally, monitoring allows for early intervention in areas where tiger numbers are declining.
Ecological Impact of Tiger Conservation
Tigers play a critical role in maintaining ecological balance. As apex predators, they regulate the populations of herbivores, preventing overgrazing that could otherwise harm plant life. This, in turn, ensures the health of entire ecosystems. The conservation of tigers is not only about saving one species but also about protecting the broader ecosystem that they inhabit. Healthy tiger populations contribute to the vitality of forests, making tiger conservation a critical part of maintaining biodiversity in India.
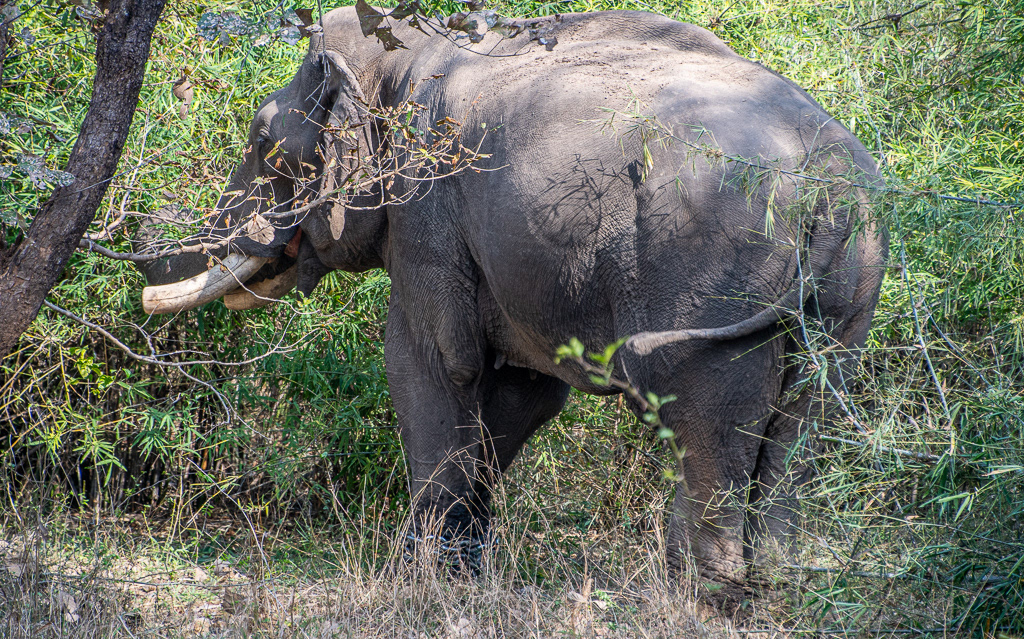
The Future of Elephants in India
Elephants are an iconic species in India, and the country is home to around 60% of the global Asian elephant population. However, the species faces various threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-elephant conflict. Elephants play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance by shaping the environment, dispersing seeds, and helping to maintain the integrity of forests and grasslands. Conservationists are working hard to ensure the survival of elephants by addressing the challenges they face and strengthening conservation efforts across the country.
The Threat of Habitat Loss and Human-Elephant Conflict
The loss of elephant habitats due to deforestation and land conversion for agriculture has led to an increase in human-elephant conflict. Elephants, in search of food and water, often wander into human settlements, leading to crop destruction and sometimes injuries or fatalities. This conflict results in a negative perception of elephants among local communities. However, conservationists have been focusing on creating wildlife corridors that allow elephants to travel safely without coming into conflict with people. These corridors not only protect elephants but also help maintain healthy ecosystems by allowing for the free movement of wildlife.
Combating Poaching and the Ivory Trade
Poaching for ivory remains one of the biggest threats to elephants. Although international trade in ivory has been banned, illegal poaching persists in some areas, often driven by the high demand for ivory. Efforts to curb poaching include the strengthening of anti-poaching laws, training of local wildlife rangers, and the use of technology for monitoring elephant populations. Increased cooperation between law enforcement agencies and conservation organizations has helped reduce poaching, but there is still much work to be done to protect these animals.
Reducing Human-Elephant Conflict
Reducing human-elephant conflict requires a multi-pronged approach. One successful strategy involves the use of electric fences, trenches, and other physical barriers to keep elephants away from agricultural areas. Additionally, local communities are being trained to handle elephants safely, and compensation schemes for crop damage have been introduced to reduce retaliation against elephants. Education programs aimed at fostering a positive relationship between people and elephants are helping build understanding and promote peaceful coexistence.
The Importance of Elephant Monitoring Programs
Monitoring elephant populations is crucial to understanding the health and movement patterns of these animals. The data gathered through satellite tracking, camera traps, and field surveys helps conservationists make informed decisions regarding elephant conservation. It also helps in the identification of critical habitats that need additional protection. Monitoring allows for targeted efforts to prevent conflicts and to ensure that the elephants’ habitat remains intact.
Ecological Role of Elephants
Elephants are considered keystone species, meaning that their actions help shape the ecosystem in profound ways. Through activities such as uprooting trees and digging waterholes, elephants create spaces for other species to thrive. They are also critical seed dispersers, helping to regenerate forests and maintain biodiversity. Protecting elephants means preserving the ecosystem services they provide, which benefits not just other wildlife, but human communities as well.
....India is home to a significant portion of the world’s tiger population, and conservation efforts over the past few decades have yielded some positive results. The population of tigers in India has increased due to various conservation programs like Project Tiger, but this success is not without its challenges. Despite the significant progress made in recent years, tigers continue to face numerous threats, including habitat degradation, illegal poaching, and conflicts with human populations. These challenges could jeopardize the extensive efforts dedicated to the conservation of these magnificent creatures.
Habitat Preservation and Fragmentation
A vital component of tiger conservation is the safeguarding of their natural habitats. India has been proactively engaged in the establishment of tiger reserves; however, these initiatives encounter significant challenges due to deforestation and land encroachment for agricultural purposes. As forests are cleared to accommodate human populations, the subsequent fragmentation of habitats markedly impacts tiger populations. Tigers require large territories to roam freely, hunt, and establish their territory. If these territories are disrupted or too fragmented, their survival becomes uncertain. Experts emphasize the need for connecting isolated forests through wildlife corridors to allow tigers to safely move between habitats.
Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade
Poaching remains one of the largest threats to tiger populations in India. The illicit trade in tiger body parts, encompassing skins, bones, and organs, perpetuates illegal poaching, irrespective of the strict regulations enacted to safeguard these majestic animals. The worldwide demand for tiger components, particularly within traditional medicine practices, renders them extremely attractive to poachers. In response, enhanced law enforcement initiatives, including the deployment of advanced technologies like camera traps and drones, have been introduced in tiger reserves. Furthermore, community involvement and educational programs are essential in fostering a protective atmosphere for tigers.
Human-Wildlife Conflict and Coexistence
The increase in human-wildlife conflict presents a significant challenge for tiger conservation. As human populations expand, tigers are increasingly drawn into agricultural regions, resulting in heightened conflict. Instances of tigers attacking livestock often provoke retaliatory actions from local farmers. This conflict not only threatens the tiger population but also creates a tense relationship between wildlife conservationists and the local community. The solution lies in creating buffer zones, where humans and wildlife can coexist safely. Measures like livestock enclosures, compensation for lost animals, and awareness campaigns are crucial in alleviating human-wildlife conflict.
Tiger Monitoring and Population Data
Monitoring tiger populations through national surveys is essential in understanding the dynamics of their numbers and overall health. The annual tiger census provides valuable data on the distribution, population, and behavior of tigers. This data helps conservationists gauge the effectiveness of current strategies and adjust them accordingly. It also helps identify areas of high tiger activity, which can be further protected or restored. Additionally, monitoring allows for early intervention in areas where tiger numbers are declining.
Ecological Impact of Tiger Conservation
Tigers play a critical role in maintaining ecological balance. As apex predators, they regulate the populations of herbivores, preventing overgrazing that could otherwise harm plant life. This, in turn, ensures the health of entire ecosystems. The conservation of tigers is not only about saving one species but also about protecting the broader ecosystem that they inhabit. Healthy tiger populations contribute to the vitality of forests, making tiger conservation a critical part of maintaining biodiversity in India.
The Future of Elephants in India
Elephants are an iconic species in India, and the country is home to around 60% of the global Asian elephant population. However, the species faces various threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-elephant conflict. Elephants play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance by shaping the environment, dispersing seeds, and helping to maintain the integrity of forests and grasslands. Conservationists are working hard to ensure the survival of elephants by addressing the challenges they face and strengthening conservation efforts across the country.
The Threat of Habitat Loss and Human-Elephant Conflict
The loss of elephant habitats due to deforestation and land conversion for agriculture has led to an increase in human-elephant conflict. Elephants, in search of food and water, often wander into human settlements, leading to crop destruction and sometimes injuries or fatalities. This conflict results in a negative perception of elephants among local communities. However, conservationists have been focusing on creating wildlife corridors that allow elephants to travel safely without coming into conflict with people. These corridors not only protect elephants but also help maintain healthy ecosystems by allowing for the free movement of wildlife.
Combating Poaching and the Ivory Trade
Poaching for ivory remains one of the biggest threats to elephants. Although international trade in ivory has been banned, illegal poaching persists in some areas, often driven by the high demand for ivory. Efforts to curb poaching include the strengthening of anti-poaching laws, training of local wildlife rangers, and the use of technology for monitoring elephant populations. Increased cooperation between law enforcement agencies and conservation organizations has helped reduce poaching, but there is still much work to be done to protect these animals.
Reducing Human-Elephant Conflict
Reducing human-elephant conflict requires a multi-pronged approach. One successful strategy involves the use of electric fences, trenches, and other physical barriers to keep elephants away from agricultural areas. Additionally, local communities are being trained to handle elephants safely, and compensation schemes for crop damage have been introduced to reduce retaliation against elephants. Education programs aimed at fostering a positive relationship between people and elephants are helping build understanding and promote peaceful coexistence.
The Importance of Elephant Monitoring Programs
Monitoring elephant populations is crucial to understanding the health and movement patterns of these animals. The data gathered through satellite tracking, camera traps, and field surveys helps conservationists make informed decisions regarding elephant conservation. It also helps in the identification of critical habitats that need additional protection. Monitoring allows for targeted efforts to prevent conflicts and to ensure that the elephants’ habitat remains intact.
Ecological Role of Elephants
Elephants are considered keystone species, meaning that their actions help shape the ecosystem in profound ways. Through activities such as uprooting trees and digging waterholes, elephants create spaces for other species to thrive. They are also critical seed dispersers, helping to regenerate forests and maintain biodiversity. Protecting elephants means preserving the ecosystem services they provide, which benefits not just other wildlife, but human communities as well.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2025-02-17
Tags: madhya-pradesh News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel





































































































.png)
 (1).png)