Home / election / Fragmented Maharashtra Poll Landscape Reflects Dec
Fragmented Maharashtra Poll Landscape Reflects Dec
By: My India Times
3 minutes read 75Updated At: 2024-11-13
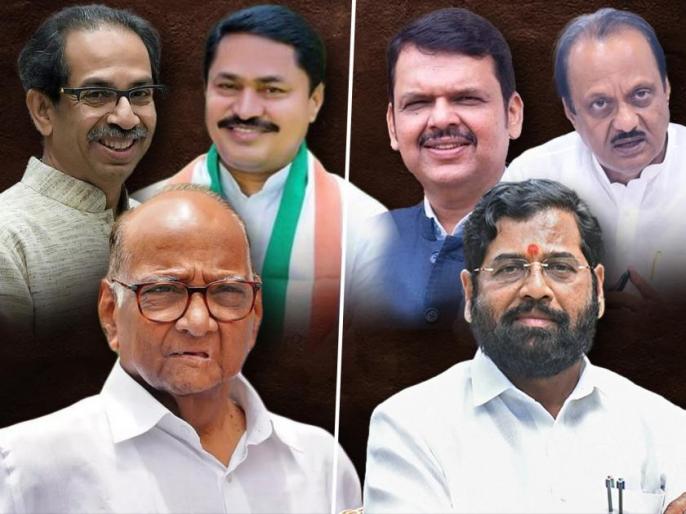

Mumbai: Maharashtra's political battleground has become one of India’s most fragmented electoral arenas, where alliances, once clear-cut, have unraveled over decades. In the latest Assembly polls, the division among major parties and the complex social dynamics at play highlight not only a unique breakdown of Maharashtra’s political system but also an electorate grappling with questions of representation, stability, and ideological clarity.
From Dominance to Division: The Erosion of Maharashtra’s Bipolarity
For decades, Maharashtra politics followed a predictable, bipolar model dominated by two major coalitions: the Congress-led alliance and the Shiv Sena-BJP combine. However, this longstanding structure began to fracture notably in the 2014 Assembly elections when the four major players — Congress, NCP, BJP, and Shiv Sena — chose to contest independently. This departure from coalition politics has led to persistent fragmentation, leaving the electorate increasingly disillusioned by perceived opportunism and a dilution of ideological commitments.
Political analysts point to this shift as a reflection of the shifting allegiances within Maharashtra’s electorate, as various factions, rather than pledging loyalty to one coalition, now pivot to issues-based politics and temporary coalitions. As a result, voters are confronted with an evolving and complex array of alliances, with regional and caste-based agendas often taking precedence over consistent party ideologies.
Historical Backbone: The Maratha-Kunbi Influence
The roots of Maharashtra’s fragmented politics lie deeply embedded in its historical power structures. Since the state’s formation in 1960, the Congress party constructed a broad-based alliance by mobilizing support from the Maratha-Kunbi caste, Dalits, and Muslims. This model, often termed "bahujan politics," was pioneered by Y.B. Chavan and yielded decades of Congress dominance. The Maratha-Kunbi group, with its control over vast agricultural resources, sugar cooperatives, and local governance, has long been a central political force.
The influence of Marathas extends beyond numbers, as their connection to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj has solidified their cultural dominance. This historical lineage reinforces their political sway, which today intersects with regional pride and Maratha identity. Yet, caste-based mobilization and identity politics have increasingly fragmented the vote, as parties seek to secure specific caste bases, leaving broad-based coalitions more elusive than ever.
Emergence of BJP and Shiv Sena: A New Political Era and Fragmentation
The rise of the BJP-Shiv Sena alliance in the 1990s introduced a new chapter in Maharashtra’s political history. Combining regional pride with a Hindutva agenda, this coalition redefined the state's political landscape. As economic liberalization took root, the Shiv Sena and BJP capitalized on rising discontent around stagnant agricultural growth and rapid industrialization, presenting a vision of pride and progress that resonated with many voters.
However, the dynamics shifted again with ideological and tactical differences between the Shiv Sena and BJP emerging over time, which culminated in an unexpected alliance shuffle, resulting in fragmented political stances and further confusing the electorate.
Social Complexity: Caste, Progress, and Representation
Despite Maharashtra's strides in social reform and economic growth, caste remains a potent force. Progressive movements, initially thought to dilute caste politics, instead complicated it. Marathas retain significant sway, yet lower-caste groups and other communities demand representation and policies that address their specific challenges. With rising demands for reservation, farmers’ rights, and economic reforms, Maharashtra’s political landscape increasingly reflects the state’s socio-economic diversity and its need for inclusive development strategies.
Fragmentation’s Impact on Voters and Maharashtra’s Future
Today, Maharashtra’s voters face a fractured political environment with a blend of regionalism, caste loyalties, and shifting party alliances. This leaves many citizens questioning which parties can provide both ideological consistency and genuine commitment to addressing the unique challenges facing Maharashtra.
Moving forward, Maharashtra’s parties face a critical test: Can they deliver clear, unified agendas that address the needs of a rapidly changing demographic landscape? Or will short-term alliances and narrow vote-bank politics continue to create an electoral maze for the state’s 124 million residents?
As the state prepares for a potentially pivotal election, the electorate’s patience with fragmented alliances is wearing thin. Maharashtra’s leaders are under pressure to move beyond temporary alliances and present a compelling, coherent vision for a state that remains one of India’s most politically complex yet economically promising regions.
....Mumbai: Maharashtra's political battleground has become one of India’s most fragmented electoral arenas, where alliances, once clear-cut, have unraveled over decades. In the latest Assembly polls, the division among major parties and the complex social dynamics at play highlight not only a unique breakdown of Maharashtra’s political system but also an electorate grappling with questions of representation, stability, and ideological clarity.
From Dominance to Division: The Erosion of Maharashtra’s Bipolarity
For decades, Maharashtra politics followed a predictable, bipolar model dominated by two major coalitions: the Congress-led alliance and the Shiv Sena-BJP combine. However, this longstanding structure began to fracture notably in the 2014 Assembly elections when the four major players — Congress, NCP, BJP, and Shiv Sena — chose to contest independently. This departure from coalition politics has led to persistent fragmentation, leaving the electorate increasingly disillusioned by perceived opportunism and a dilution of ideological commitments.
Political analysts point to this shift as a reflection of the shifting allegiances within Maharashtra’s electorate, as various factions, rather than pledging loyalty to one coalition, now pivot to issues-based politics and temporary coalitions. As a result, voters are confronted with an evolving and complex array of alliances, with regional and caste-based agendas often taking precedence over consistent party ideologies.
Historical Backbone: The Maratha-Kunbi Influence
The roots of Maharashtra’s fragmented politics lie deeply embedded in its historical power structures. Since the state’s formation in 1960, the Congress party constructed a broad-based alliance by mobilizing support from the Maratha-Kunbi caste, Dalits, and Muslims. This model, often termed "bahujan politics," was pioneered by Y.B. Chavan and yielded decades of Congress dominance. The Maratha-Kunbi group, with its control over vast agricultural resources, sugar cooperatives, and local governance, has long been a central political force.
The influence of Marathas extends beyond numbers, as their connection to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj has solidified their cultural dominance. This historical lineage reinforces their political sway, which today intersects with regional pride and Maratha identity. Yet, caste-based mobilization and identity politics have increasingly fragmented the vote, as parties seek to secure specific caste bases, leaving broad-based coalitions more elusive than ever.
Emergence of BJP and Shiv Sena: A New Political Era and Fragmentation
The rise of the BJP-Shiv Sena alliance in the 1990s introduced a new chapter in Maharashtra’s political history. Combining regional pride with a Hindutva agenda, this coalition redefined the state's political landscape. As economic liberalization took root, the Shiv Sena and BJP capitalized on rising discontent around stagnant agricultural growth and rapid industrialization, presenting a vision of pride and progress that resonated with many voters.
However, the dynamics shifted again with ideological and tactical differences between the Shiv Sena and BJP emerging over time, which culminated in an unexpected alliance shuffle, resulting in fragmented political stances and further confusing the electorate.
Social Complexity: Caste, Progress, and Representation
Despite Maharashtra's strides in social reform and economic growth, caste remains a potent force. Progressive movements, initially thought to dilute caste politics, instead complicated it. Marathas retain significant sway, yet lower-caste groups and other communities demand representation and policies that address their specific challenges. With rising demands for reservation, farmers’ rights, and economic reforms, Maharashtra’s political landscape increasingly reflects the state’s socio-economic diversity and its need for inclusive development strategies.
Fragmentation’s Impact on Voters and Maharashtra’s Future
Today, Maharashtra’s voters face a fractured political environment with a blend of regionalism, caste loyalties, and shifting party alliances. This leaves many citizens questioning which parties can provide both ideological consistency and genuine commitment to addressing the unique challenges facing Maharashtra.
Moving forward, Maharashtra’s parties face a critical test: Can they deliver clear, unified agendas that address the needs of a rapidly changing demographic landscape? Or will short-term alliances and narrow vote-bank politics continue to create an electoral maze for the state’s 124 million residents?
As the state prepares for a potentially pivotal election, the electorate’s patience with fragmented alliances is wearing thin. Maharashtra’s leaders are under pressure to move beyond temporary alliances and present a compelling, coherent vision for a state that remains one of India’s most politically complex yet economically promising regions.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2024-11-13
Tags: election News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel




































































































.png)
 (1).png)