Home / editorials / Strengthening Local Government Support to Combat the Growing PFAS Contamination Crisis
Strengthening Local Government Support to Combat the Growing PFAS Contamination Crisis
By: My India Times
3 minutes read 44Updated At: 2025-02-13

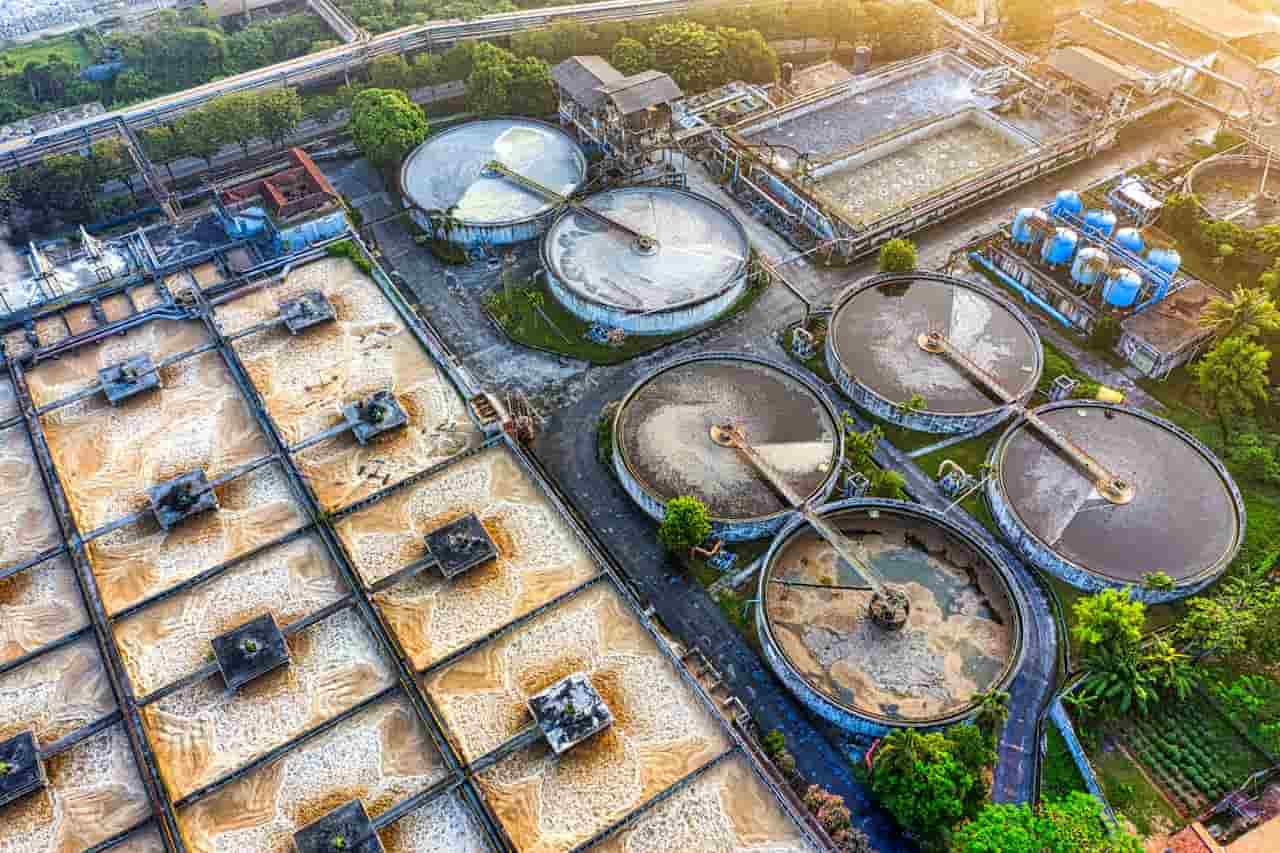
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), often termed "forever chemicals" due to their persistent nature, have become a focal point of environmental and health concerns globally. These synthetic compounds, known for their water- and oil-repellent characteristics, are commonly found in a range of consumer goods such as non-stick cookware, waterproof apparel, and firefighting foams. Their resistance to degradation leads to environmental accumulation and bioaccumulation in humans, which may present potential health risks including cancer, immune system compromise, and developmental issues in children.
Japan's Efforts to Address PFAS Contamination
In Japan, the government has proactively addressed PFAS contamination. A nationwide survey conducted by the Environment Ministry and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism between May and September 2024 assessed PFAS levels in tap water across 3,755 water suppliers. The analysis indicates that by September 30, 2024, no water suppliers were found to have PFAS concentrations exceeding the provisional threshold of 50 nanograms per liter, a guideline established in 2020. This result implies that strategies such as the alteration of water sources have been successful in reducing contamination levels.
Plans for Stricter Regulations
Despite these positive results, the government recognizes the need for more stringent regulations. In December 2024, the Environment Ministry announced plans to establish a legal standard for PFAS concentrations in tap water, transitioning from the current provisional target to a binding regulation by April 2026. This change will mandate regular testing by water suppliers and require immediate corrective actions if PFAS levels exceed the set standard.
Global Trends in PFAS Regulation
The international community is also intensifying efforts to regulate PFAS. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed strict new drinking water limits for six types of PFAS, aiming to set maximum contaminant levels near zero. This initiative reflects growing concerns about the health impacts of these substances and underscores the global movement toward stricter regulatory frameworks.
Evaluation of Japan’s Current Standards
While Japan's current provisional limit aligns with international standards, the government is considering further tightening these regulations. An expert panel is evaluating whether to make it mandatory for local governments and water suppliers to take immediate action when PFAS levels exceed the established limits. This deliberation includes assessing the readiness of local authorities to implement necessary measures and the potential need for support in terms of resources and infrastructure.
Challenges in Implementing PFAS Regulations
The effectiveness of these regulatory measures hinges on the capacity of local governments and water suppliers to monitor and manage PFAS contamination. Regular testing, prompt reporting, and swift remediation are essential components of a robust response strategy. However, these tasks can be resource-intensive, particularly for smaller municipalities with limited budgets and technical expertise.
Need for Government Support
To address these challenges, the national government must provide comprehensive support to local entities. This assistance could include financial aid to cover the costs of advanced testing equipment and remediation technologies, as well as technical guidance to ensure that local personnel are adequately trained to handle PFAS-related issues. Additionally, establishing a centralized database for reporting PFAS levels could facilitate better coordination and more effective responses across different regions.
Importance of Public Awareness
Public awareness and engagement are also critical. Informing communities about the potential risks associated with PFAS and the steps being taken to mitigate these risks can foster public trust and encourage community involvement in monitoring efforts. Educational campaigns can empower residents to take precautionary measures, such as using certified water filters and properly disposing of products containing PFAS.
....Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), often termed "forever chemicals" due to their persistent nature, have become a focal point of environmental and health concerns globally. These synthetic compounds, known for their water- and oil-repellent characteristics, are commonly found in a range of consumer goods such as non-stick cookware, waterproof apparel, and firefighting foams. Their resistance to degradation leads to environmental accumulation and bioaccumulation in humans, which may present potential health risks including cancer, immune system compromise, and developmental issues in children.
Japan's Efforts to Address PFAS Contamination
In Japan, the government has proactively addressed PFAS contamination. A nationwide survey conducted by the Environment Ministry and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism between May and September 2024 assessed PFAS levels in tap water across 3,755 water suppliers. The analysis indicates that by September 30, 2024, no water suppliers were found to have PFAS concentrations exceeding the provisional threshold of 50 nanograms per liter, a guideline established in 2020. This result implies that strategies such as the alteration of water sources have been successful in reducing contamination levels.
Plans for Stricter Regulations
Despite these positive results, the government recognizes the need for more stringent regulations. In December 2024, the Environment Ministry announced plans to establish a legal standard for PFAS concentrations in tap water, transitioning from the current provisional target to a binding regulation by April 2026. This change will mandate regular testing by water suppliers and require immediate corrective actions if PFAS levels exceed the set standard.
Global Trends in PFAS Regulation
The international community is also intensifying efforts to regulate PFAS. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed strict new drinking water limits for six types of PFAS, aiming to set maximum contaminant levels near zero. This initiative reflects growing concerns about the health impacts of these substances and underscores the global movement toward stricter regulatory frameworks.
Evaluation of Japan’s Current Standards
While Japan's current provisional limit aligns with international standards, the government is considering further tightening these regulations. An expert panel is evaluating whether to make it mandatory for local governments and water suppliers to take immediate action when PFAS levels exceed the established limits. This deliberation includes assessing the readiness of local authorities to implement necessary measures and the potential need for support in terms of resources and infrastructure.
Challenges in Implementing PFAS Regulations
The effectiveness of these regulatory measures hinges on the capacity of local governments and water suppliers to monitor and manage PFAS contamination. Regular testing, prompt reporting, and swift remediation are essential components of a robust response strategy. However, these tasks can be resource-intensive, particularly for smaller municipalities with limited budgets and technical expertise.
Need for Government Support
To address these challenges, the national government must provide comprehensive support to local entities. This assistance could include financial aid to cover the costs of advanced testing equipment and remediation technologies, as well as technical guidance to ensure that local personnel are adequately trained to handle PFAS-related issues. Additionally, establishing a centralized database for reporting PFAS levels could facilitate better coordination and more effective responses across different regions.
Importance of Public Awareness
Public awareness and engagement are also critical. Informing communities about the potential risks associated with PFAS and the steps being taken to mitigate these risks can foster public trust and encourage community involvement in monitoring efforts. Educational campaigns can empower residents to take precautionary measures, such as using certified water filters and properly disposing of products containing PFAS.
By: My India Times
Updated At: 2025-02-13
Tags: editorials News | My India Times News | Trending News | Travel News
Join our WhatsApp Channel




































































































.png)
 (1).png)